What Do Tbones and Porterhouse Cuts Come From on Beef
 Beefiness Cuts (American terminology) | |
| Type | Brusque loin and tenderloin cut of beefiness |
|---|---|

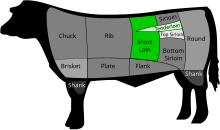
The T-bone and porterhouse are steaks of beef cut from the short loin (chosen the sirloin in Commonwealth countries and Ireland). Both steaks include a "T"-shaped lumbar vertebra with sections of intestinal internal oblique musculus on each side. Porterhouse steaks are cut from the rear end of the short loin and thus include more tenderloin steak, forth with (on the other side of the bone) a large strip steak. T-bone steaks are cut closer to the front, and contain a smaller section of tenderloin. The smaller portion of a T-bone, when sold alone, is known as a filet mignon (called fillet steak in Commonwealth countries and Ireland), especially if cut from the small-scale forward stop of the tenderloin.
Experts differ nearly how big the tenderloin must be to differentiate T-bone steak from porterhouse. The United States Department of Agronomics's Institutional Meat Purchase Specifications state that the tenderloin of a porterhouse must be at least 1.25 inches (32 mm) broad at its widest, while that of a T-os must be at least 0.5 inches (13 mm) wide. [1] However, steaks with a large tenderloin are oftentimes called a "T-bone" in restaurants despite technically beingness porterhouse.
Owing to their large size, and as they contain meat from two of the nigh prized cuts of beef (the short loin and the tenderloin), T-bone steaks are generally considered one of the highest quality steaks, and prices at steakhouses are accordingly loftier. Porterhouse steaks are fifty-fifty more highly valued owing to their larger tenderloin.
In British usage, followed in the Commonwealth countries, "porterhouse" often means a British sirloin steak (i.e. US strip steak) on the bone, i.e. without the tenderloin on the other side of T-bone. Some British on-line butchers also offering American style porterhouse steaks.
In New Zealand and Commonwealth of australia, a porterhouse is sirloin steak (strip steak in USA) off the os.
Beefcake of the T-bone [edit]
To cutting a T-bone from butchered cattle, a lumbar vertebra is sawn in half through the vertebral column. The downwardly prong of the 'T' is a transverse process of the vertebra, and the flesh surrounding it is the spinal muscles. The pocket-sized semicircle at the top of the 'T' is half of the vertebral foramen.
Preparation [edit]

Florentine steak in Florence, Italian republic
T-os and porterhouse steaks are suited to fast, dry oestrus cooking methods, such as grilling or broiling. Since they contain a small amount of collagen relative to other cuts, longer cooking times are not necessary to tenderize the meat. There is some contention equally to whether the os conducts heat within the meat so that it cooks more evenly and prevents meat drying out and shrinking during cooking,[2] [three] or the meat near the bone will cook more slowly than the rest of the steak,[4] and the tenderloin will tend to reach the desired temperature before the strip.[v] [half-dozen]
Bistecca alla fiorentina [edit]
Bistecca alla fiorentina, or 'beefsteak Florentine style', consists of a T-bone traditionally sourced from either the Chianina or Maremmana breeds of cattle. A favorite of Tuscan cuisine, the steak is grilled over a wood or charcoal fire, seasoned with salt, sometimes with black pepper, and olive oil, applied immediately after the meat is retired from the heat. Thickly cut and very large, "Bistecca" are oft shared betwixt two or more than persons, and traditionally served very rare, sometimes garnished with lemon wedges, if non accompanied by cherry vino, and accompanied past Tuscan beans every bit a side dish.[7]
Cotoletta di Vitello alla Milanese [edit]
The same cut of meat, only from a calf, is used for Cotoletta alla milanese, which consists of one.v cm-thick cuts which are dilapidated in breadcrumbs and fried in clarified butter with salt.
Run into also [edit]
- Listing of steak dishes
- Meat on the os
- Rib center steak
References [edit]
- ^ United States Department of Agronomics (November 2014). Institutional Meat Purchase Specifications (PDF). Fresh Beef Series 100. p. 68. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 Dec 2016. Retrieved xviii June 2021.
- ^ Delia Smith:Lamb Archived November 23, 2010, at the Wayback Car
- ^ LBC:Cooking in the credit crunch Archived 2011-07-27 at the Wayback Automobile
- ^ "Buy T Os Steak | T-Bone Steak for Sale U.k.". Consume Great Meat . Retrieved 2020-08-14 .
- ^ King (Née Turner), Nicola J.; Whyte, Rosemary (2006). "Does It Wait Cooked? A Review of Factors That Influence Cooked Meat Color". Journal of Nutrient Science. 71 (iv): R31–R40. CiteSeerX10.1.1.668.6042. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2006.00029.x.
- ^ Serious Eats (30 May 2014). "How to Grill a T-Bone Steak". Archived from the original on iv March 2016. Retrieved five March 2016.
- ^ Waverly Root, The Food of Italy, 1971, ISBN 0-394-72429-i.
External links [edit]
- "USDA Institutional Meat Buy Specifications". Archived from the original on 2014-08-06. Retrieved 2022-03-ten . (687 KiB)
- "Beef Cuts Chart" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-05-03. Retrieved 2011-12-12 .
- Porter House proper name origin article
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T-bone_steak#:~:text=Unsourced%20material%20may%20be%20challenged%20and%20removed.&text=The%20T%2Dbone%20and%20porterhouse,oblique%20muscle%20on%20each%20side.
0 Response to "What Do Tbones and Porterhouse Cuts Come From on Beef"
Post a Comment